Opal – Mineral and Healing Properties
Chemistry: SiO2 – nH2O; Hydrated Silicon Dioxide.
Class: Mineraloids
Group: Some minerologists place Opal in the Quartz Group.
Uses: As a gemstone and ornamental stone.
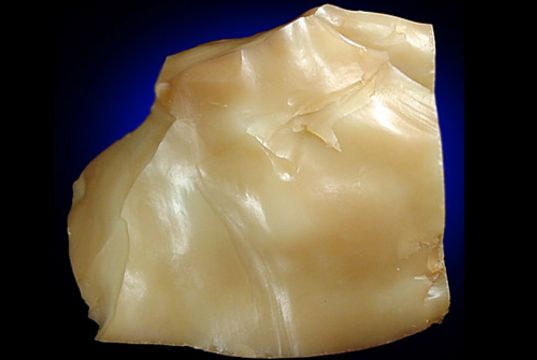
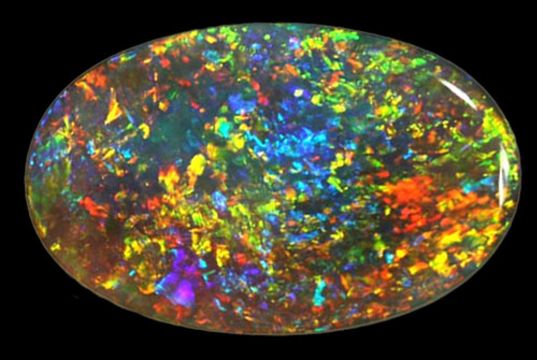

Opal’s internal structure makes it diffract light; depending on the conditions in which it formed it can take on many colors. Opal ranges from clear through white, gray, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, magenta, rose, pink, slate, olive, brown, and black. Of these hues, the reds against black are the most rare, whereas white and greens are the most common. It varies in optical density from opaque to semi-transparent. For gemstone use, its natural color is often enhanced by placing thin layers of opal on a darker underlying stone, like basalt.
Origin Of The Name
The word opal is adapted from the Roman term opalus, but the origin of this word is a matter of debate. However, most modern references suggest it is adapted from the Sanskrit word £pala.
References to the gem are made by Pliny the Elder. It is suggested it was adapted it from Ops, the wife of Saturn and goddess of fertility. The portion of Saturnalia devoted to Ops was “Opalia”, similar to opalus.
Another common claim that the term is adapted from the Greek word, opillos. This word has two meanings, one is related to “seeing” and forms the basis of the English words like “opaque”, the other is “other” as in “alias” and “alter”. It is claimed that opalus combined these uses, meaning “to see a change in color”. However, historians have noted that the first appearances of opillos do not occur until after the Romans had taken over the Greek states in 180 B.C., and they had previously used the term paederos.
However, the argument for the Sanskrit origin is strong. The term first appears in Roman references around 250 B.C., at a time when the opal was valued above all other gems. The opals were supplied by traders from the Bosporus, who claimed the gems were being supplied from India. Before this the stone was referred to by a variety of names, but these fell from use after 250.
Interesting Facts
Green Opals are deposited at a relatively low temperature and may occur in the fissures of almost any kind of rock, being most commonly found with limonite, sandstone, Rhyolite, marl and basalt.
Opal is the national gemstone of Australia, which produces 97% of the world’s supply.
It has been mined for centuries, at least since Roman times when they extracted the opal from areas now within the Czech Republic. The Aztecs made use of local Mexican sources as did the Spaniards when they exported the material back to Europe.
In late 2008, NASA announced that it had discovered opal deposits on Mars.
The world’s largest and most valuable gem opal “Olympic Australis” was found in August 1956 at the “Eight Mile” opal field in Coober Pedy. It weighs 17,000 carats and is 11 inches long, with a height of 43 inches and a width of 41 inches . It is valued at $2,500,000
Miocene age opalised teeth, bones, fish, and a snake head have been found.
Where Is It Found
Australia produces around 97% of the world’s opal. 90% is called ‘light opal’ or white and crystal opal. White makes up 60% of the opal productions but cannot be found in all of the opal fields. Crystal opal or pure hydrated silica makes up 30% of the opal produced, 8% is black and only 2% is boulder opal.
The town of Coober Pedy in South Australia is a major source of opal.
Mintabie Opal Fields located approximately 250 km north west of Coober Pedy has also produced large quantities of Crystal opal and also the rarer black opal. The black opal is said to be some of the best examples found in Australia.
Andamooka in South Australia is also a major producer of matrix opal, crystal opal, and black opal. Boulder opal consists of concretions and fracture fillings in a dark siliceous ironstone matrix. It is found sporadically in western Queensland, from Kynuna in the north, to Yowah and Koroit in the south.
The rarest type of Australian opal is “pipe” opal, closely related to boulder opal, which forms in sandstone with some iron-ore content, usually as fossilized tree roots. Its largest quantities are found around Jundah in South West Queensland. Australia also has opalised fossil remains, including dinosaur bones in New South Wales, and marine creatures in South Australia.
The Virgin Valley opal fields of Humboldt County in northern Nevada produce a wide variety of precious black, crystal, white, fire, and lemon opal. The black fire opal is the official gemstone of Nevada. Most of the precious opal is partial wood replacement.
Some of the opal has high water content and may desiccate and crack when dried. The largest black opal in the Smithsonian Institution comes from the Royal Peacock opal mine in the Virgin Valley.
Another source of white base opal or creamy opal in the United States is Spencer, Idaho. Other significant deposits of precious opal around the world can be found in the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Turkey, Indonesia, Brazil, Honduras, Guatemala, Nicaragua and Ethiopia.
What Do We Do With It
Opal is considered the birthstone for people born in October or under the sign of Scorpio and Libra. Opals are used almost solely for jewelry, gemstones and mineral collecting.
Metaphysical Uses
Green opals help give an energy boost. Green Opal, in particular, is a cleansing and rejuvenating gemstone that gives meaning to life and brings about spiritual perspective, while strengthening the immune system. Opal helps amplify our traits and characteristics, allowing us to recognize and feel the creativity within ourselves. It helps allow us to release our inhibitions, strengthen our memories, brings faithfulness and loyalty to our personal and business relationships.
Known as the stone of happy dreams and changes bringing to us the understanding and acceptance of our inherent perfection. It has been used to awaken psychic and mystical qualities. Opal with fire inside it can help encourage our intuition and insight.
Physical Characteristics
Color: Colorless, white, yellow, red, orange, green, brown, black, blue.
Luster: Subvitreous to uneven.
Transparency: Opaque, translucent, transparent.
Crystal System: Amorphous
Crystal Habits: Irregluar veins, in masses, in nodules.
Cleavage: None
Fracture: Concoidal to uneven
Hardness: 5.5 – 6
Specific Gravity: 2.15
Streak: White
Associated Minerals: Chert, volcanic rock and many others.
Best Field Indicators: Color play & opalescence, low density, fluorescence, fracture filling tendency and lack of cleavage or crystal faces.


